Scientific Name
Ornithorhynchus anatinus
Also Called: Duck-mole
Description
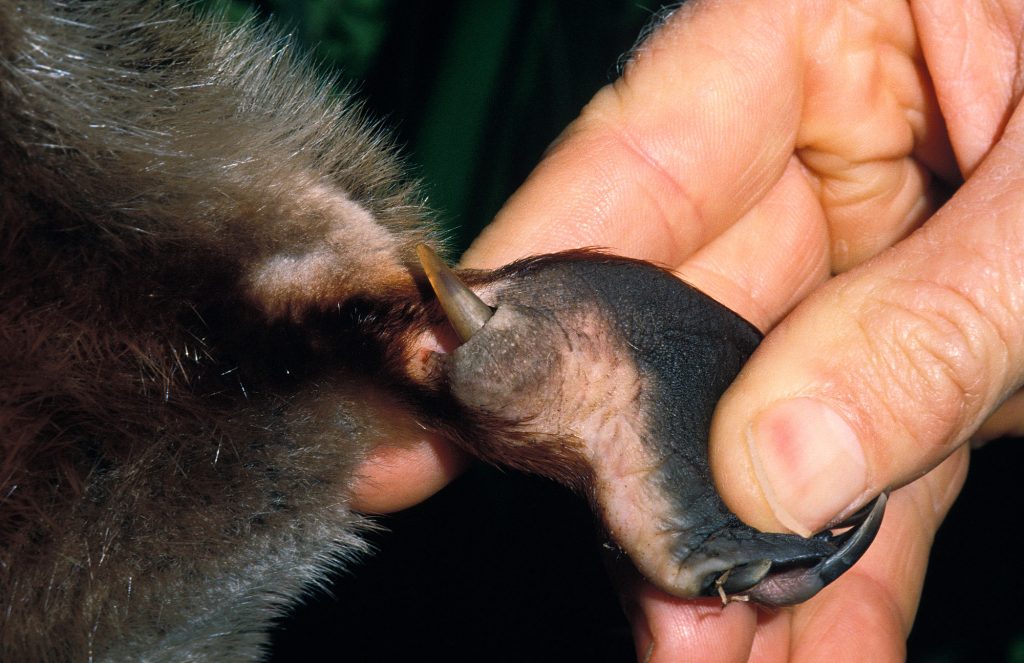
The platypus has a flat, streamlined body. They have a muzzle shaped like the bill of a duck, webbed feet, and a tail like that of a beaver. The bill is not hard like that of a bird. It is actually an elongated muzzle covered with a leathery skin. The bill and feet of a platypus are black while the fur is usually a dark brown color. The platypus also possesses a spur on it hind legs that can be used to inject venom into another creature. In man this usually causes agonizing pain but can be fatal to smaller creatures.
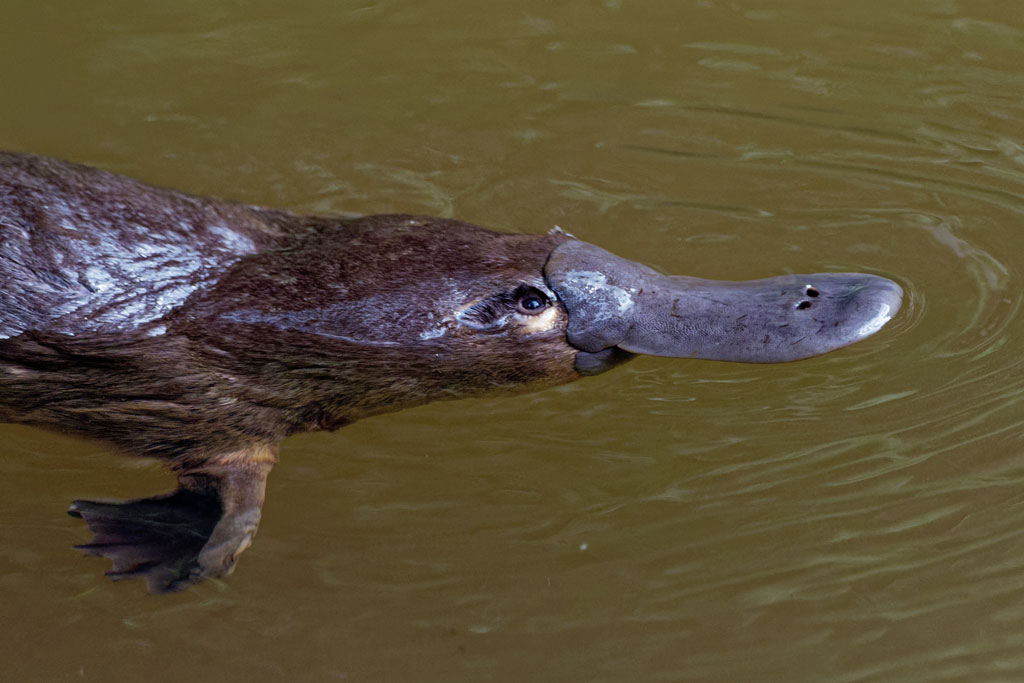
The platypus forages for food by diving underwater for up to 1.5 minutes and searching for food. While underwater, it stores any food it finds in cheek pouches. On surfacing, it sorts out what it found and eats it. When searching for food, the platypus is relying solely on its electrically sensitive bill to find food. The bill of a platypus can detect small electrical currents put out by the creatures that it eats. The platypus is a strong swimmer though not very fast. It swims by alternating movements of its front feet only. When out of the water, the webbing folds between its toes. The fur of the platypus is some of the most waterproof in the animal kingdom and the tail is used to store fat.
Food
The platypus eats insect larvae as well as freshwater shrimp, bivalve mollusks, frogs and fish eggs.
Habitat
The platypus is found in Eastern Australia in freshwater streams and rivers. Platypus live in burrows that they dig along the banks of streams and rivers that they use as a food source.
Predators
Hawks, eagles, owls, crocodiles, water-rats, pythons, goannas, foxes, dogs, and cats make up the predators of the platypus.
Social Structure
The platypus is primarily nocturnal. It is also a solitary animal and usually only comes together to mate (although you can often find several animals in the same general area.) During mating season, it is not unusual for male platypuses to become very aggressive. However, the platypus is usually a shy and wary animal.

Birth & Offspring
The platypus is one of only two mammals that do not give birth to live young but lays eggs instead (the other is the echidna.) After birth, the young live on milk provided by the mother. However, the platypus does not have nipples. Instead, glands along the side of the mother secrete milk and the young platypus will lap it up. After six weeks the young have fur and may leave the nest for short periods. They are weaned by five months old.
Senses
The platypus has an electro-sensitive bill. They also have excellent senses of sight and hearing.

Lydia King is a huge animal lover and has always been fascinated with learning about the animal kingdom. She enjoys writing about anything animal related from scientific information about rare species to animal references in pop culture.












